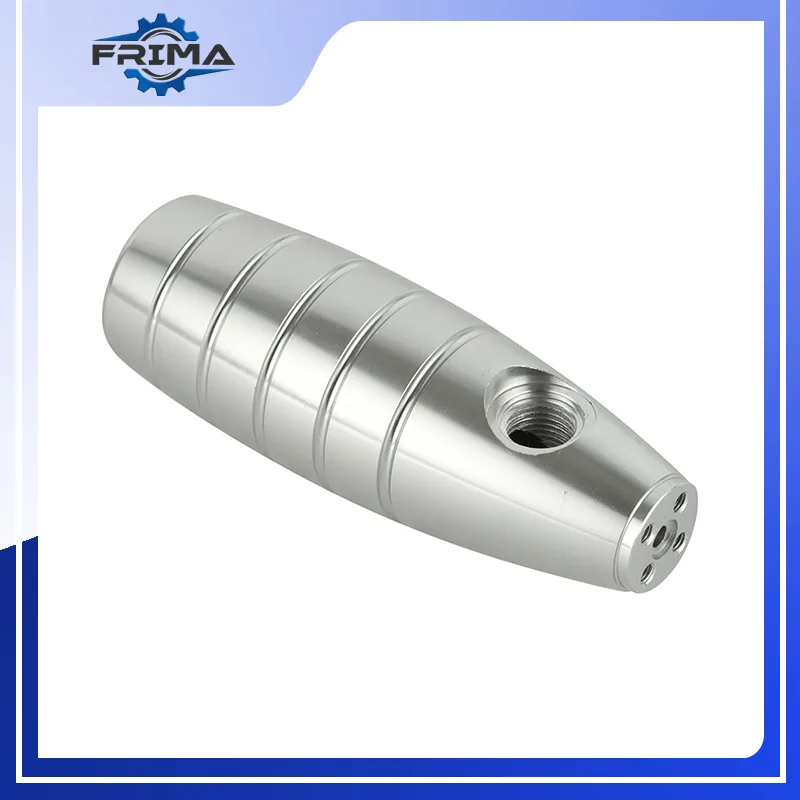
Overview
Customized Precision Machining Automotive Parts
CNC Precision Machining Automotive Parts is a component or assembly that has been manufactured by machining, a process that removes material from the workpiece using cutting tools. Machined parts are used in a variety of industries, including the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries.
CNC automotive machined parts can be made from a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. The type of material used will depend on the application of the part.
What specification of Customized Precision Machining Automotive Parts FRIMA can offer?
1. Size
- Threaded Holes
- UNC & UNF threads from #2 up to 0.5 in.
- Metric threads M1.2 and above.
2. Radii
Turned outside corners will typically include a 0.005 in. chamfer.
Minimum hole size:
- Minimum on-axis and axial: 0.04 in. (1mm)
- Minimum radial: 0.08 in. (0.5mm), 0.04 in (0.5mm) for aluminum and brass
3. Grooves:
- Minimum OD groove width: 0.047 in. (1.2mm)
- Minimum OD groove width for aluminum and brass:0.019 in (0.5mm)
- Maximum OD groove depth: 0.95 in. (24.1mm)—varies with a groove width
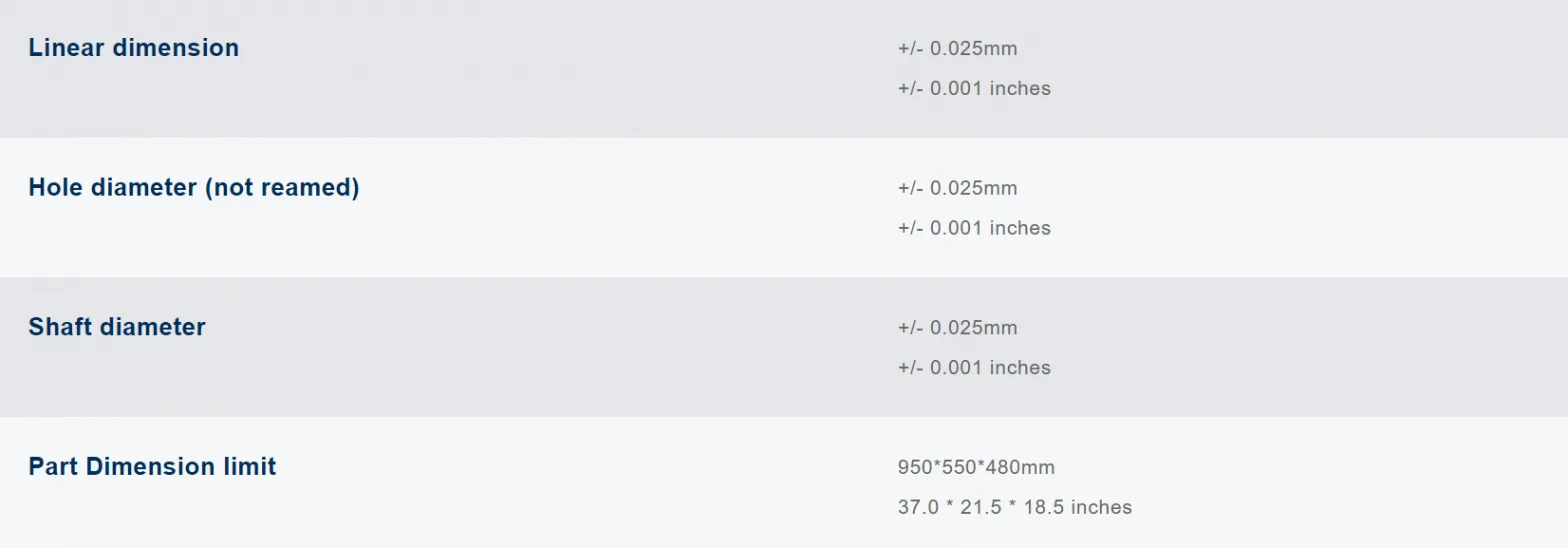
4. Customized Precision Machining Automotive Parts Standards
| CNC Machining Standards (DIN ISO 2768-1(1991-06) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerance class | tolerance(mm) | |||||||||||||
| Metal (ISO 2768-F) | Plastic (ISO 2768-F) | |||||||||||||
| 0.5 to 3 | Over 3 to 6 | Over 6 to 30 | Over 30 to 120 | Over 120 to 400 | Over 400 to 1000 | Over 1000 to 2000 | 0.5 to 3 | Over 3 to 6 | Over 6 to 30 | Over 30 to 120 | Over 120 to 400 | Over 400 to 1000 | Over 1000 to 2000 | |
| F | ±0.05 | ±0.05 | ±0.1 | ±0.15 | ±0.2 | ±0.3 | ±0.5 | ±0.05 | ±0.05 | ±0.1 | ±0.15 | ±0.2 | ±0.3 | ±0.5 |
Show All
5. General Tolerances For Shape And Position
| General tolerances for shape and position (DIN ISO 2768-2(1991-04) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerance class | tolerance(mm) | |||||||||||||
| Straightness and Flatness | Verticality | Symmetry | ||||||||||||
| 10 | 10 to 30 | 30 to 100 | 100 to 300 | 300 to 1000 | 1000 to 3000 | to 100 | 100 to 300 | 300 to 1000 | 1000 to 3000 | to 100 | 100 to 300 | 300 to 1000 | 1000 to 3000 | |
| H | ±0.02 | ±0.05 | ±0.1 | ±0.2 | ±0.3 | ±0.4 | ±0.2 | ±0.3 | ±0.4 | ±0.5 | ±0.5 | |||
Show All
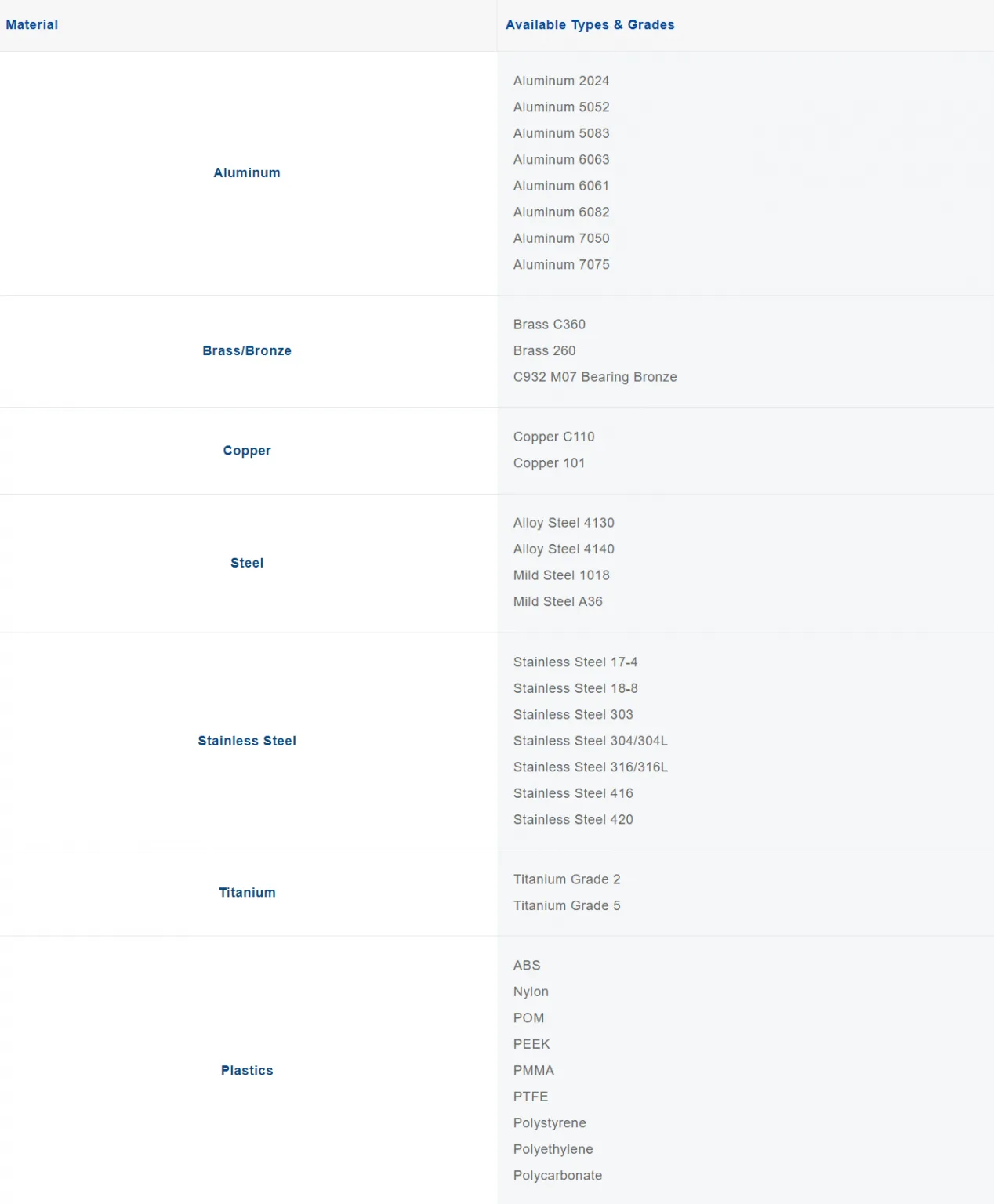
Materials Used for CNC Precision Machining Automotive Parts
Customized Precision Machining Automotive Parts can be applied to various materials, including metal, plastic, and wood. Different lathes are needed for turning metal and wood. According to the types of machined part materials, certain maintenance and safety precautions may be required for the lathe.
Here are some common materials for precision machining automotive parts below. If the material you required is not listed in the table, please contact us.
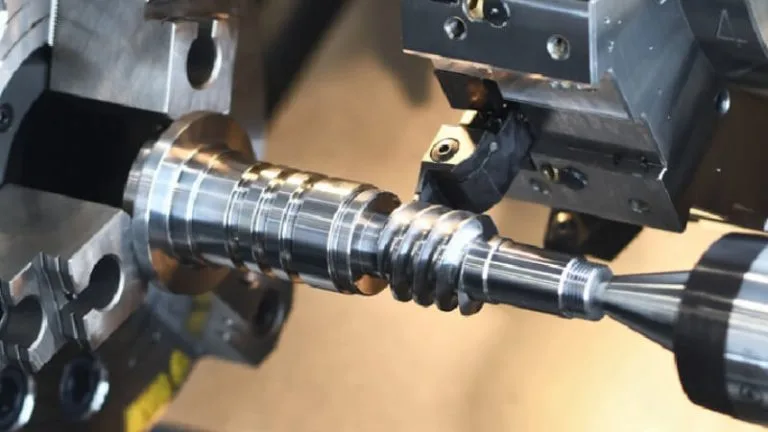

Surface Finish at FRIMA – Process for Customized Precision Machining Automotive Parts
Here is a wide selection of metal surface finishing services of your choice for the machined precision machining automotive parts to improve the part appearance, surface smoothness, corrosion resistance, and other characteristics.
| As machined | Description |
|---|---|
| As machined | Standard finish with a surface roughness of 1.6 μm (126 μin). |
| Smoothing | The standard smoothing surface roughness (Ra) is 0.8 μm (63 μin). |
| Painting | Spraying paint, pigment, or color to a solid surface as a colored protective layer. |
| Passivation | Remove ferrous contaminants or use a light coat of protective material to create a shell. |
| Powder Coating | A functional and decorative finish that is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder. |
| Anodizing | Type II (anodizing color or clear) or Type III (anodizing hard coat) |
| Polishing | Produce a smooth and shiny surface. |
| Black Oxide | Formed a black conversion coating on metal parts. |
| Bead Blasting | Removing surface deposits by applying fine glass beads at high pressure. |
| Abrasive Blasting/Sandblasting | Smoothing and cleaning a hard surface by forcing solid particles across that surface. |
| Electroplating/Plating | Form a thin coherent metal coating on an electrode. |
| Brushing | Polishing the metal with grit results in a unidirectional satin finish. |
| Chromate Conversion coating | Increase the corrosion resistance while maintaining conductive properties |
Show All




